
Meditation and techniques to manage stress.But, in conjunction with other treatment, joining a support group and sharing your experiences with others could benefit you. A support group alone is not a substitute for therapy. In addition to psychotherapy or medication, there are other ways that you may benefit from when dealing with an anxiety disorder. If you have an anxiety disorder, you should work with your doctor to choose the best treatment for you. Seek help early if you are experiencing symptoms that don’t go away.Our social interactions have been limited during the last few months but talking with friends over the phone and doing things that you enjoy while staying safe may help reduce your worries.Make it a priority to get a good night’s sleep, since poor sleep quality, insomnia, or sleep deprivation may increase your risks.Avoid alcohol or drug use since it can cause or worsen anxiety.While you can’t predict what will cause anxiety disorders to develop, you can take the following steps to help reduce the impact of symptoms if you are anxious: Take steps to avoid the feared object or situation.Experience immediate, intense anxiety upon encountering the feared object or situation.Endure unavoidable objects and situations with intense anxiety or dread.Experience an irrational or excessive worry about encountering the feared object or situation.People with phobias feel fear that is out of proportion to the actual danger caused by that situation or object. Common phobias include flying and heights, but people can develop phobias regarding almost anything. Sensations of shortness of breath, smothering, or chokingĪ phobia is an intense fear caused by a specific object or situation.Heart palpitations, a pounding heartbeat, or an accelerated heart rate.A person with panic disorder has repeated and unexpected panic attacks, and often worries about when the next attack will happen.ĭuring a panic attack, some people may experience: Over time, they can be triggered by certain situations. Panic attacks are periods of intense fear that can occur suddenly. Trouble falling or staying asleep, restlessness, or unsatisfying sleep.Difficulty controlling feelings of worry.In some cases, people with GAD have experienced these feelings since childhood or adolescence, while in other cases, they may have been triggered by temporary stress. These feelings can cause problems in areas of your life such as school, work, and social interactions. It can cause a loss of consciousness and sometimes cardiac arrest and sudden death when associated with heart disease.Įach type of anxiety disorder has its own unique symptoms:Ī person with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) has frequent or constant feelings of worry and anxiety about issues, such as health, work, social interactions, or everyday situations. Ventricular tachycardia - This rapid heartbeat starts in the lower heart chambers.Symptoms include an overly fast pulse and dizziness. Supraventricular tachycardia - A rapid heart rate above the lower heart chambers.There may be no symptoms, or chest pain, palpitations, and shortness of breath. It could lead to serious clotting conditions or stroke. The result can be an erratic heartbeat that interferes with blood flow. Atrial fibrillation - This is the most common type of arrhythmia.The doctor monitors your heart and then uses that information to tell if the arrhythmia is one of the following: You could have to use the monitor for just a few days, but in some cases, you may need to use or wear it for over a month. If you go to your regular doctor, you may be referred to a specialist, called a cardiologist, who may send you home with a device to monitor your heart rate.

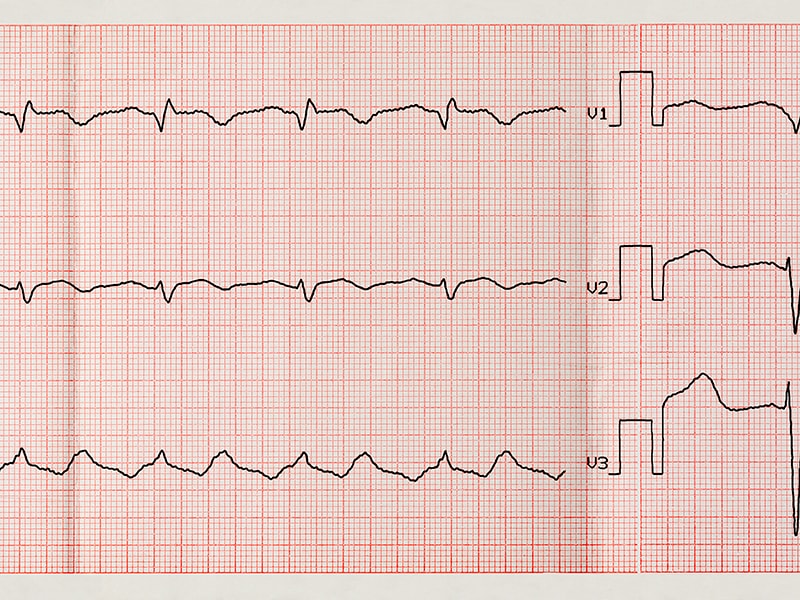
Types of ArrhythmiaĪrrhythmia is classified by the type of heartbeat and where they occur. The heart palpitations could be a sign of anemia, an overactive thyroid gland, or an irregular heartbeat, also called an arrhythmia. Get emergency help if the palpitations include: Seek medical attention if there is a family history of heart disease, if palpitations happen with increasing frequency, or become more forceful. Take note of when they happen because there might be a triggering event, and that could be worth mentioning at your next checkup. Most palpitations happen infrequently and last just a few seconds.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
